Frank and I are looking to update the vSphere Clustering deep dive to vSphere 7. While scoping the work I stumbled on to something interesting, and this is the change that was introduced for the vSphere HA restart mechanism, and specifically the placement of VMs in vSphere 7. In previous releases vSphere HA had a straight forward way of doing placement for VMs when VMs need to be restarted as a result of a failure. In vSphere 7.0 this mechanism was completely overhauled.
So how did it work pre-vSphere 7?
- HA uses the cluster configuration
- HA uses the latest compatibility list it received from vCenter
- HA leverages a local copy of the DRS algorithm with a basic (fake) set of stats and runs the VMs through the algorithm
- HA receives a placement recommendation from the local algorithm and restarts the VM on the suggested host
- Within 5 minutes DRS runs within vCenter, and will very likely move the VM to a different host based on actual load
As you can imagine this is far from optimal. So what is introduced in vSphere 7? Well, we introduce two different ways of doing placement for restarts in vSphere 7:
- Remote Placement Engine
- Simple Placement Engine
The Remote Placement Engine, in short, is the ability for vSphere HA to make a call to DRS for the recommendation of the placement of a VM. This will take the current load of the cluster, the VM happiness, and all configured affinity/anti-affinity/vm-host affinity rules into consideration! Will this result in a much slower restart? The great thing is that the DRS algorithm has been optimized over the past years and it is so fast that there will not be a noticeable difference between the old mechanism and the new mechanism. Added benefit of course for the engineering team is that they can remove the local DRS module, which means there’s less code to maintain. How this works is that the FDM Master communicated with the FDM Manager which runs in vCenter Server. FDM Manager communicates with the DRS service to request a placement recommendation.
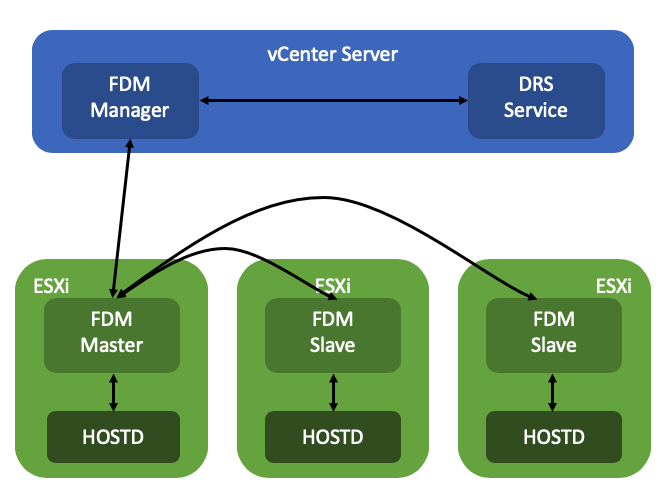
Now some of you will probably wonder what happens when vCenter Server is unavailable, well this is where the Simple Placement Engine comes into play. The team has developed a new placement engine that basically takes a round-robin approach, but does consider of course “must rules” (VM to Host) and the compatibility list. Note, affinity, or anti-affinity rules, are not considered when SPE is used instead of RPE! This is a known limitation, which is considered to be fixed in the future. If a host, for instance, is not connected to the datastore the VM is running on that needs to be restarted than that host is excluded from the list of potential placement targets. By the way, before I forget, version 7 also introduced a vCenter heartbeat mechanism as a result. HA will be heart beating the vCenter Server instance to understand when it will need to resort to the Simple Placement Engine vs the Remote Placement Engine.
I dug through the FDM log to find some proof of these new mechanisms, (/var/log/fdm.log) and found an entry that shows there are indeed two placement engines:
Invoking the RPE + SPE Placement Engine
RPE stands for “remote placement engine”, and SPE for “simple placement engine”. Where Remote of course refers to DRS. You may ask yourself, how do you know if DRS is being called? Well, that is something you can see in the logs in the DRS log files, when a placement request is received, the below entry shows up in the log file:
FdmWaitForUpdates-vim.ClusterComputeResource:domain-c8-26307464
This even happens when DRS is disabled and also when you use a license edition which does not include DRS even, which is really cool if you ask me. If for whatever reason vCenter Server is unavailable, and as a result DRS can’t be called, you will see this mentioned in the FDM log, and as shown below, it will use the Simple Placement Engine’s recommendation for the placement of the VM:
Invoke the placement service to process the placement update from SPE
A cool and very useful small HA enhancement if you ask me for vSphere 7.0!
** Disclaimer: This article contains references to the words master and/or slave. I recognize these as exclusionary words. The words are used in this article for consistency because it’s currently the words that appear in the software, in the UI, and in the log files. When the software is updated to remove the words, this article will be updated to be in alignment. **
 Last week I saw an update from one of the Clumio founders on twitter. It reminded me that I had promised to take a look at their product. This week I had a meeting set up with Clumio and we went over their product and how to configure it briefly. Clumio is a SaaS based backup solution that was founded in 2017 by former PernixData, Nutanix, EMC folks. The three founders are Poojan Kumar, Kaustubh Patil, and Woon Jung, and those three you may remember from PernixData. One thing to point out is that they had 3 rounds of funding (~190 million dollars) so far and they came out of stealth around VMworld 2019. Coincidentally they won the Gold award for Best of VMworld in the data protection category, and best of show for the entire show, not bad for a first VMworld. I guess that I have to point out that although I would classify them as backup/recovery today, they are adding new functionality weekly and “backup/recovery” is probably not a fair category, data protection is more appropriate and it would not surprise me if that evolves to data management and protection over time. If you are not a fan of reading, simply head over to my youtube video on Clumio, otherwise, just continue below.
Last week I saw an update from one of the Clumio founders on twitter. It reminded me that I had promised to take a look at their product. This week I had a meeting set up with Clumio and we went over their product and how to configure it briefly. Clumio is a SaaS based backup solution that was founded in 2017 by former PernixData, Nutanix, EMC folks. The three founders are Poojan Kumar, Kaustubh Patil, and Woon Jung, and those three you may remember from PernixData. One thing to point out is that they had 3 rounds of funding (~190 million dollars) so far and they came out of stealth around VMworld 2019. Coincidentally they won the Gold award for Best of VMworld in the data protection category, and best of show for the entire show, not bad for a first VMworld. I guess that I have to point out that although I would classify them as backup/recovery today, they are adding new functionality weekly and “backup/recovery” is probably not a fair category, data protection is more appropriate and it would not surprise me if that evolves to data management and protection over time. If you are not a fan of reading, simply head over to my youtube video on Clumio, otherwise, just continue below.




