VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 was recently launched, and that means vSAN 9.0 is also available. There are many new features introduced in 9.0, so a perfect time to ask Pete Koehler to join the podcast once again and go over some of these key enhancements. Below, you can find the links we discussed during the episode, as well as the embedded player to listen to the episode. Alternatively, you can also listen to the episode via Spotify, Apple, or any other podcast app you may use. Make sure to like and subscribe!
express storage architecture
Where’s my vSAN Data Protection screen in 8.0 U3?
 The first time I deployed vSphere/vSAN 8.0 U3 I immediately looked for the vSAN Data Protection UI. I always get excited about new features, and simply want to test it. I mean who doesn’t like scalable snapshots and a great way of managing snapshot schedules? Finally available within the vSphere Client! Of course, I could not find it, but I figured that was because I was on some weird alpha build of the product. Now that the product has shipped, it must be there out of the box, right?
The first time I deployed vSphere/vSAN 8.0 U3 I immediately looked for the vSAN Data Protection UI. I always get excited about new features, and simply want to test it. I mean who doesn’t like scalable snapshots and a great way of managing snapshot schedules? Finally available within the vSphere Client! Of course, I could not find it, but I figured that was because I was on some weird alpha build of the product. Now that the product has shipped, it must be there out of the box, right?
No it isn’t. You will need to deploy an appliance in order for this functionality to appear in the UI. The appliance can be found under “Drivers and Tools” under the vSphere Hypervisor download (Which is under VMware vSphere), it is called “VMware vSAN Snapshot Service Appliance”. The current version is named “snapservice_appliance-8.0.3.0-24057802_OVF10.ova”. You need to deploy this OVA, and I would highly recommend to request a DNS name for it and have it properly registered. I fiddled around with the hosts file on VCSA and forgot to add the name to my local host file on my laptop, and had some weird issues as a result, which I am trying to reproduce at the moment, I will report back if/when I can.
The other thing to point out is the following, the documentation tells you to download the certs and copy the text for the Appliance, it isn’t something most of us do daily either, you can simply open a web browser and use the following url “https://<name of your vCenter server>/certs/download.zip” to download the certs and then unzip the downloaded file. (More details to be found here.) It will contain the certs, and if you open the cert with a proper text editor you can copy/paste that into the deployment screen for the OVA. (Yes, I know there are other ways as well, but I found this one to be the easiest.)
Now, when you deployed the OVA, and when everything is configured correctly, you should see a successful task, or actually two: download plugin, deploy plug, as shown in the next screenshot.

If you do get the “error downloading plug-in” error message, it likely is one of two things:
- DNS / Hosts files are not correctly configured, resulting in the URL not being reachable. Make sure you can resolve the URL!
- Cert thumbprint was incorrectly copied/pasted. Use this document to fix the issue.
Okay, now that I got the appliance up and running, I will probably do a follow-up post on what you can do with it 🙂
vSAN ESA and the minimum number of hosts with RAID-1/5/6
I had a meeting last week with a customer and a question came up around the minimum number of hosts a cluster requires in order to use. particular RAID configuration for vSAN. I created a table for the customer and a quick paragraph on how this works and figured I would share it here as well.
With vSAN ESA VMware introduced a new feature called “Adaptive RAID-5”. I described this feature in this blog post here. In short, depending on the size of the cluster a RAID-5 configuration will either be a 2+1 scheme or a 4+1 scheme. There’s no longer a 3+1 scheme with vSAN ESA. Of course, there’s still the ability to use RAID-1 and RAID-6 as well, the RAID-1 and RAID-6 schemes remained unchanged.
When it comes to vSAN ESA, below are the number of hosts required for a particular RAID scheme. Do note, that with RAID-5, of the size of the cluster changes (higher of lower) then the scheme may also change as described in the linked article above.
| Failures To Tolerate | Object Configuration | Minimum number of hosts | Capacity of VM size |
|---|---|---|---|
| No data redundancy | RAID-0 | 1 | 100% |
| 1 Failure (Mirroring) | RAID-1 | 3 | 200% |
| 1 Failure (Erasure Coding) | RAID-5, 2+1 | 3 | 150% |
| 1 Failure (Erasure Coding) | RAID-5, 4+1 | 6 | 125% |
| 2 Failures (Erasure Coding) | RAID-6, 4+2 | 6 | 150% |
| 2 Failures (Mirorring) | RAID-1 | 5 | 300% |
| 3 Failures (Mirorring) | RAID-1 | 7 | 400% |
vSAN ReadyNode emulated configurations? What are those?
Last week Pete Koehler dropped a bomb on us when he blogged about vSAN ReadyNode emulated configurations. Since then I had a few folks asking what this exactly is. It is fairly simple, some vendors have special SKUs for ReadyNodes, which doesn’t always make configuring a ReadyNode to the desired specifications based on the minimum requirements for vSAN ESA and the supported components. SAY WHAT?
Well just imagine you are a Dell shop and you want to use the R750. You simply check if the R750 is listed on the VCG, you list the minimum CPU spec and you go from there based on the minimum (and maximum) specifications for vSAN ESA and based on your workload profile. Just as an example, the minimum specifications for vSAN ESA are now as follows with the introduction of the vSAN AF-0 ReadyNode configuration:
- Minimum of 16 cores Intel or AMD
- For example: 2 x Intel Xeon® Gold 6334 3.6G, 8 cores
- Or: 1 x AMD EPYC 9124 16C 200W 3.0GHz Processor
- Minimum of 128GB memory
- Minimum of 10GbE
- Minimum of 2 NVMe Devices (as listed on vSAN VCG) and 3.2TB per host
Now that we know what those minimums are, I could simply go to the Dell website and spec a Dell R750 Server as desired. This server could have for instance:
- 2 x Intel® Xeon Gold 6342 2.8G, 24 cores
- 256GB memory
- 25GbE networking
- 6 x Dell Ent NVMe CM6 RI 3.84TB
Even though it is not on the list as a ReadyNode configuration, this configuration would be supported as all the components are certified, and the server itself is also certified as a vSAN ReadyNode platform, and we are following the guidelines as documented in the vSAN ESA RN KB.
I hope this helps those who are going through the process of procuring hardware for vSAN ESA.
Scalable Snapshots demo with the vSAN 8.0 Express Storage Architecture
Starting with vSAN 8 a brand new architecture was introduced called “Express Storage Architecture”. Over the last year or so a lot of information has been shared about ESA and the benefits of ESA. One of the things which ESA introduces is much-improved snapshot scalability.
With vSAN OSA, and with VMFS, when you create a snapshot you typically immediately see a performance degradation. This is because both VMFS and vSAN OSA still operate using the redo-log based snapshot mechanism. This means that with vSAN OSA when you create a snapshot a new object is created and writes are re-directed. It also means that reads will be coming from various files, if you have one or more snapshots. This mechanism is, unfortunately, not very effective. Let me borrow a diagram that is part of a post John Nicholson wrote to demonstrate that old logic.
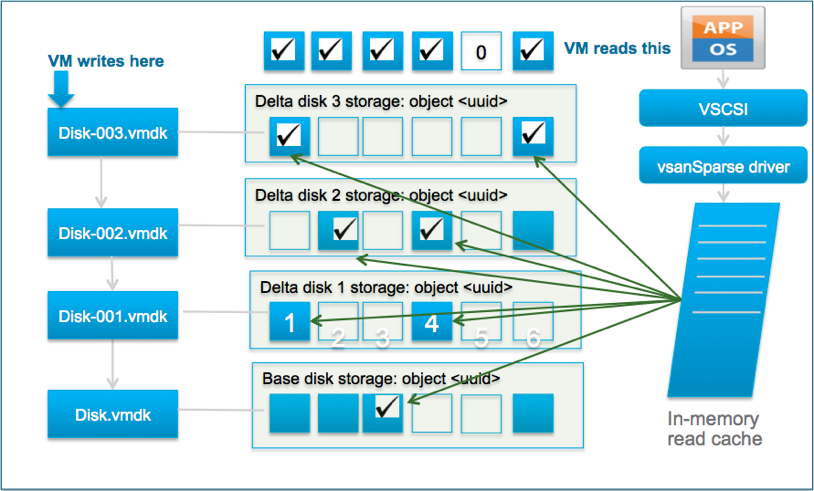
With vSAN 8 ESA the mechanism has changed and no longer does vSAN, or vSphere for that matter, create an additional object. vSAN ESA handles this on a meta-data level. In other words, instead of redirecting writes and traversing files for reads, vSAN now leverages a highly efficient B-Tree structure and pointers to keep track of which block is associated with which snapshot.
Not only is this more efficient from a capacity perspective, but more importantly it is very efficient from a performance standpoint. I ran half a dozen tests in my lab, and what I saw was a below 2% performance impact between a VM without a snapshot and a VM with one or multiple snapshots. I could NOT see a significant difference between the first or the fifth snapshot. I do want to point out that my lab is not officially certified to run vSAN ESA, nevertheless, I was very impressed with the results.
During the last run, I actually recorded the whole exercise. In this demo, I show the creation of one snapshot, while the VM is running a benchmark (HCIBench). Now, during the testing, I created not one but various snapshots and of course, I deleted all of them as well. You have all probably experienced extensive stun times during the deletion of a snapshot at times, and this is where vSAN ESA shines. The stun times have been reduced by 100 times, and that is something I am sure each of you will appreciate. Why have they been reduced drastically? Well, simply because we no longer have to copy data from one vSAN object to another. This makes a huge difference, not just for stun times, but also for performance in general (latency, IOPS, throughput). If you are interested, have a look at the demo!